Dysfunctional Supine Curl Up Functional Movement Test
This dysfunctional movement test can be best addressed by first mobilizing any ERS spinal dysfunctions that are found in the lower thoracic spine and thoracolumbar junction that restrict spinal flexion followed by stretching the erector spinae muscles. These inhibitory influences should be addressed before attempting to retrain this dysfunctional test.
It is also sometimes helpful to stretch the hip flexors as covered in #3b and c.
Anatomy and Biomechanical Considerations:
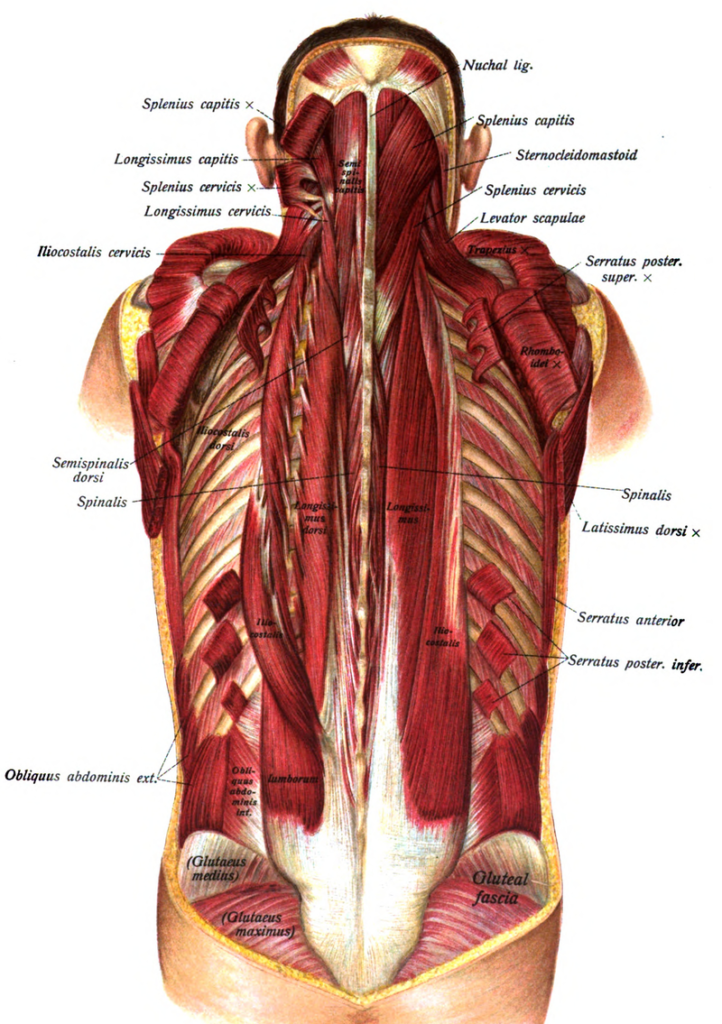
The erector spinae muscles consist of the longissimus thoracis and iliocostalis thoracis and iliocostalis lumborum muscles. These muscles working unilaterally rotate the spine to the ipsilateral side and when working bilaterally they extend the spine. The longissimus thoracis muscle becomes hypertonic when there is a non-neutral dysfunction in the thoracic spine. This hypertonicity, which is often seen unilaterally, results in inhibition of the abdominals and interferes with the ability to perform a curl up and/or reverse the lumbar lordosis during forward flexion.