Dysfunctional Trunk Rotation and/or Dysfunctional Hip Abduction Functional Movement Tests
These dysfunctional movement tests can be best addressed by mobilizing any spinal dysfunctions that are found at the thoracolumbar junction and/or by stretching the quadratus lumborum and piriformis muscles. It is also sometimes helpful to mobilize the inferiomedial hip capsule and stretch the hip adductors as covered in 4b. These sources of inhibition should be addressed before attempting retraining.
Anatomy and Biomechanical Considerations:
Quadratus Lumborum, Piriformis and Posterior Hip Capsule
Observations:
- Hypertonicity in the quadratus lumborum on one side is associated with a FRS dysfunction at the TL junction on that side, i.e., hypertonic right QL found with an FRS R at T12-L1.
- Pinching in the anterior groin with FADIR test or when attempting to stretch the piriformis is related to a tight posterior hip capsule. “Groin pain is posterior hip capsule tightness until proven otherwise”, Dr. Philip Greenman.
- An apparent tightness in the posterior hip capsule dissipates, often times dramatically, after mobilizing the upper lumbar spine for FRS dysfunctions on the same side, ie., tight R posterior hip capsule, FRS R at L1,2 or L2,3 will be present.
- Therefore, before we treat the quadratus lumborum, piriformis and posterior hip capsule we need to first identify and treat any FRS dysfunctions found between T12-L2.
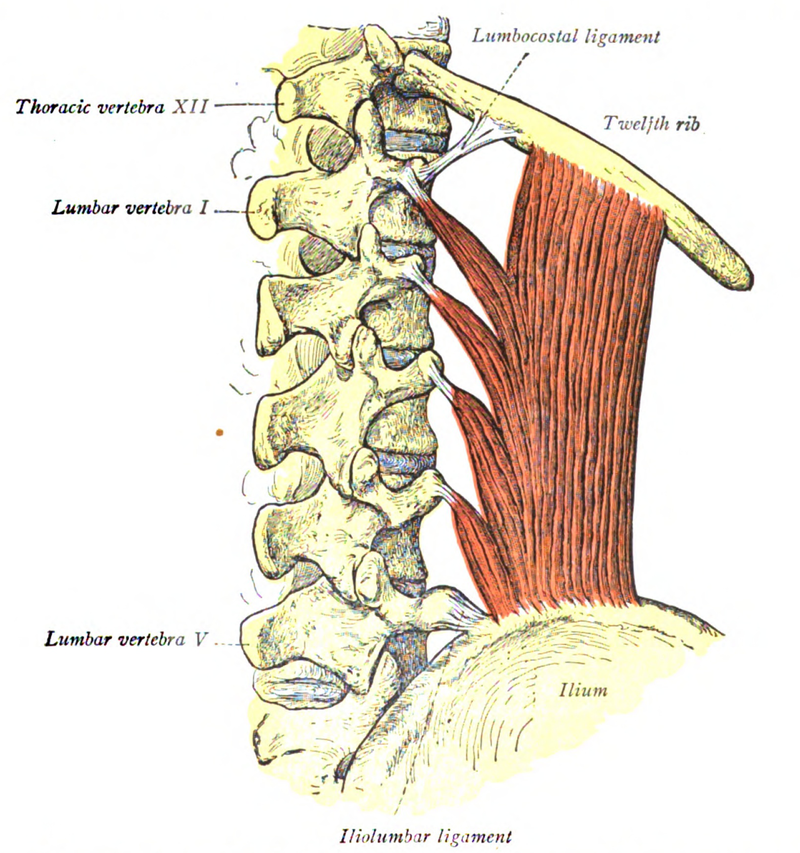
Quadratus Lumborum
- Three distinct divisions:
- Lateral (global mobilizer)
- Iliolumbar
- Lumbocostal
- Function – stabilizer of the lumbar supine, a lateral flexor of the lumbar spine and a hip hiker
- Innervation – thoraco-lumbar spinal nerves
- Most frequent muscular cause of back pain (Travell and Simons, 1992)
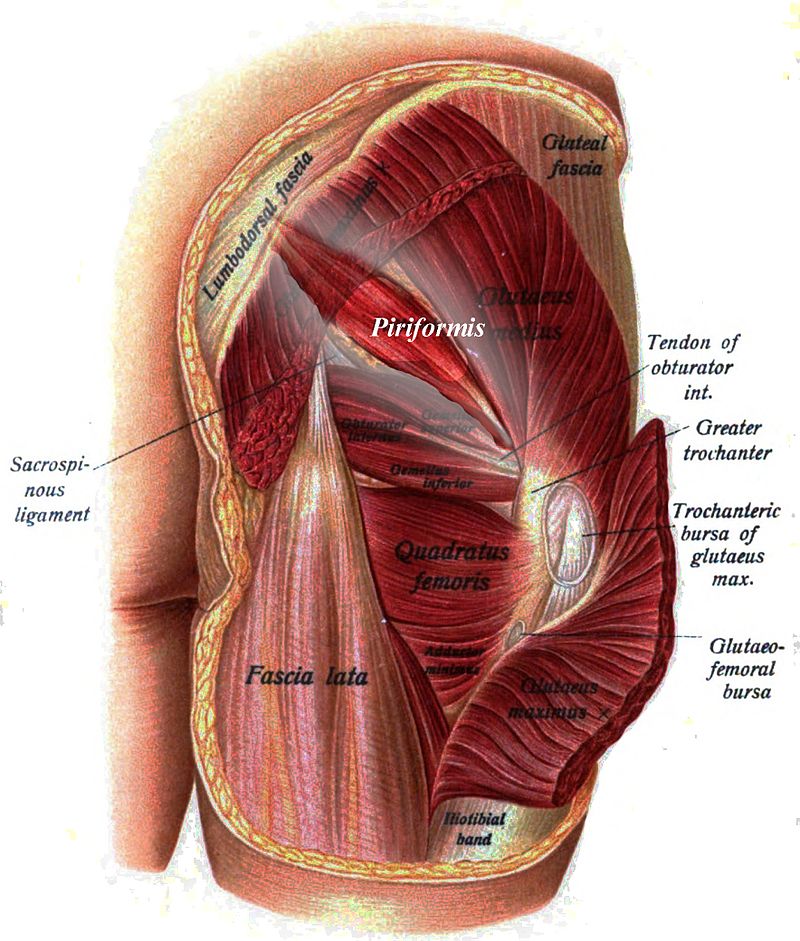
PIRIFORMIS: Origin at S 2-4, exits to insert at greater trochanter.
It crosses the SI joint and hypothetically influences the oblique axis of the sacrum during coupled motion.
- Attaches to the anterior surface of S2, 3, 4 and
inserts into the greater trochanter - Below 90º of hip flexion it abducts and ER the hip
- Above 90º of hip flexion it abducts and IR the hip
- Innervation – S1 and 2
FIVE EXTERNAL ROTATORS OF HIP
Obturator internus
Obturator externus
Gemellus superior
Gemellus inferior
Quadratus femoris
(These muscles are intimately attached to the posterior hip capsule.)